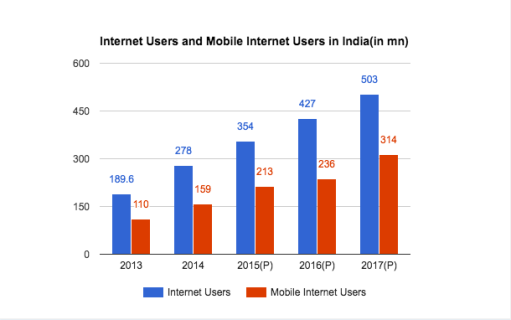
Snapchat added Snapchat stories in October 2013 while Instagram added Instagram Stories in August 2016. In a time frame of less than 1 year, Instagram Stories has not only surpassed Snapchat Stories in terms of daily active users but Instagram Stories has also widened its lead over Snapchat Stories with Instagram Stories clocking 250 million daily active users in May 2017, up from 200 million daily active users in April 2107, 150 million DAU in Jnauary 2017 and 100 mn DAU in October 2016. In contrast Snapchat Stories had total 166 mn Daily Active Users in May 2017.
Till now Instagram has very successfully cloned many of Snapchat features such as stories, location filters, custom geofilters, AR stickers, create your own stickers, scisssors. Instagram has been so successful in cloning Snapchat features that it is said that Instagram innovates through Snapchat. At the same time, it is also very true that many of innovations in Snap have come through the acquisitions made by Snapchat over the years. This blog discusses some of acquisitions made by Snapchat and how these acquisitions made an impact over the features rolled out by Snap over the years
1. Zenly
Snapchat bought social map app Zenly for between $250M and $350M in May 2017. Snapchat’s newest feature Snap Map is based on social mapping app Zenly. Snap Map is a location sharing and location based content discovery feature which is quite similar to Zenly’s social Map.
With Snap Map, one can view Snaps of sporting events, celebrations, breaking news and more from around the world by just tapping anywhere on the map to view snaps that were submitted to Our Story. If a user sees something amazing, he or she can add the Snap to Our Story and this snap could appear on the map. Similarly, Stories can be viewed on Snap Map by tapping circular thumbnails on the map. Thus, Snap Map is useful tool to explore the world, see what is happening around one self, find one’s friends and see is happening around one’s friend. Actionmojis representing friend’s location appear on map if one’s friends share their location on the Snap Map.
Snapchat Snap Map can be seen below:
2. Looksery
Snapchat acquired Looksery in April 2015 in $79.4 million total purchase consideration and additional $71.2 million in terms of stock units and cash payments. Looksery powers SnapChat’s most famous augmented reality lenses.
Snapchat Lenses are one of the most popular features on Snapchat, where lenses, real time 3D special effects such as masks, designs and graphics, are digitally superimposed on face when snapping with front faced camera. Snapchat’s Lenses are said to Snap’s attempt to bring augmented reality to users devices though in not real sense. These animated lenses are assumed to increase engagement and retention of the app users.
3. Vergence Labs
Snapchat secretly acquired Google glass competitor Vergence Lab, a Google Glass type startup, by paying $15 million that included $11 million in cash and $4 million in equity.
Snapchat’s Spectacles are based on Vergence Labs, which developed camera glasses called as Epiphany Eyewear. Epiphany wear, like Spectacles could record videos using a button. Spectacles has sun glasses with video camera that snaps 10 second clip for use in Snapchat app and have the ability to record and share HD video directly to the cloud.
Spectacle gives a small glimpse of Snap’s goal to become a camera company and bring augmented reality features to Snapchat users. Snapchat has been discretely working on augmented reality hardware device similar in line to Google Glass and Spectacles is Snap’s second attempt to bring augmented reality to users, first being Snapchat lenses.
4. Seene
Snapchat acquired a R&D driven computer vision software company for $47.0 million in 2016. Seene is a computer vision company, which specializes in 3D scene reconstruction, 3D face capture, SLAM and object tracking and augmented reality. In other words, Seene enables mobile devices to locate themselves in space, map visual environments, and recreate in 3D what is seen through the camera, turning a standard smartphone into a 3D scanner without the use of additional hardware or off-device processing.
Seene has a number of AR use cases like Seene can scan and reconstructs full 3D geometry on one’s mobile device. Further, Seene can scan and recreate 3D objects on the go and allows users make 3D selfies.
3D geometry with virtual experience using Seene:
Snapchat can also make good use of Seene’s 3D reconstruction technology in its recently launched Snapchat World Lenses, which paints the world around us into new 3D experiences. Snapchat’s World Lenses take forward Snapchat’s exploration of augmented reality from earlier Snapchat Lenses. User can switch between different lense options (different captions, Bitmoji poses or AR snapchat emojis graphics like happy rainbow, sad cloud, sassy coffee mug) and add captions, color, and Bitmoji to the world around himself. After user puts the selected lense object on the screen, the app behaves as if the lense object exists in the real world.
Snapchat new World Lense can be seen below:
5. Bitstrips
Snapchat acquired Bitstrips, a web and mobile application that allows users to create a personal avatar, in March 2016 in $64.2 million. Snapchat’s Bitmoji Stickers are based on its acquisition Bitstrips. Bitmoji Stickers are SnapChat’s personal avatar stickers. Bitmoji is personal emoji that can be sent to other Snapchat users as a sticker in Chat and on Snaps.
6. Vurb
Snapchat acquired Vurb, a mobile search company, in August 2016 for around $114.5 million. Snapchat’s Search for Stories feature is based on its acquisition Vurb. The search feature allows users find relevant Stories using specific keywords from its curated publicly shared stories shared by users and brands. The search feature identifies what is happening in all the Stories submitted by identifying elements of image or by words included in captions. This will make content discovery on Snapchat users easier.
7. Scan.me
QR snapcodes are based on its acquisition Scan.me. User can create a unique Snapcode for a website, which opens inside Snapchat when a user scan the snapcode with app’s camera. This may help websites, businesses, brands and any Snapchat users promote themselves using Snapcodes instead of URLs.
Snapchat introduced QR code for profiles based on Scan.me technology wherein people could add or follow each other on Snapchat by just scanning their friend’s Snapcode using their Snapchat camera. Concept of Snapcode was pioneered by WeChat and later popularized by Snapchat and Facebook. Later Snapchat allowed people customize their Snapcode with GIFs and download a vector version of Snapcode for printing on posters, apparels etc. Later Snapchat also introduced a feature where people can unlock snapchat filters and lenses by scnning a snapcode.
8. Cimagine
Snapchat acquired augmented reality Isralie startup Cimagine by paying $30 million to $40 million. Cimagine specializes in computer vision, real time image processing and augmented reality. Cimagine’s augmented reality platform lets consumers visualize products and thus it has great potential in e commerce where it can facilitate shopping through Snapchat. This will bring additional revenue opportunities for Snapchat where Snapchat can have partnerships with brands, departmental stores and retialers and tap Cimagine augmented reality technology to real world experience to users making digital purchase and thus boost these brands website and mobile digital sale conversion.
9. Flite
Snapchat acquihired ad tech company Flite that is primarily focused on creating digital content such as 360-degree video ads and vertical video ads for smartphones. Flites other product includes immersive ads with interactive content that scrolls and tilts; social amplification that turns status updates into paid display ads; shoppable ads that shorten the path to purchase; and localization based on geography and weather. Snapchat runs vertical video ads in its app and thus this acquisition will bring additional ad revenue to Snap and help marketers launch, manage, measure and optimize ad campaigns on real time basis.